C++对象内存布局–gdb初探
继承、多态是OOP中两大特性。C++号称是面向对象的语言,自然也要支持上面的两种设计特性。这里主要探究g++中对这两大特性的支持——vtables。大部分内容参考自 C++ vtables 。
多态与继承–vtable的作用
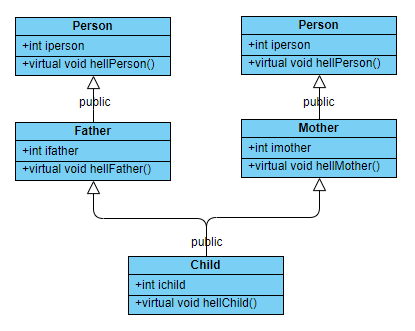
在本小节的讨论中, 我们使用如下的继承体系:
1 |
|
gdb设置
使用g++对上面的代码进行编译,以及gdb设置断点
1 | $ g++ -g multi-inher.cpp -o multi-inher |
child变量内存布局
查看child变量的内存布局1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30(gdb) call sizeof(Child)
$1 = 40
(gdb) x/48xb &child
0x7fffffffe1c0: 0xd0 0x0c 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x7fffffffe1c8: 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x02 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x7fffffffe1d0: 0xf8 0x0c 0x40 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x7fffffffe1d8: 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x03 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x7fffffffe1e0: 0x04 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xff 0x7f 0x00 0x00
0x7fffffffe1e8: 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
(gdb) p child
$2 = (Child) {
<Father> = {
<Person> = {
_vptr.Person = 0x400cd0 <vtable for Child+16>,
iPerson = 1
},
members of Father:
iFather = 2
},
<Mother> = {
<Person> = {
_vptr.Person = 0x400cf8 <vtable for Child+56>,
iPerson = 1
},
members of Mother:
iMother = 3
},
members of Child:
iChild = 4
}
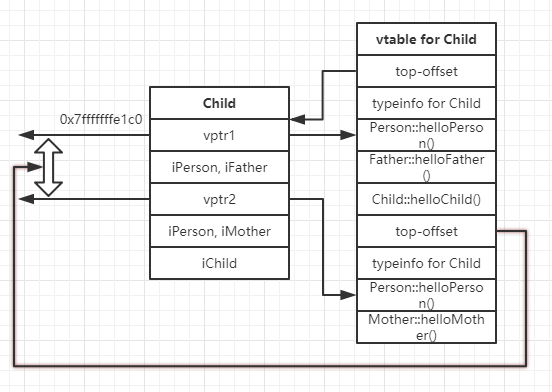
从x/48xb &child的输出,我们可以观察到Child的大小为40, child变量的内存地址在: 0x0x7fffffffe1c0,而且貌似这些内存位置上面对应的值是一些地址,看看这些地址对应的symbol是什么。
1 | (gdb) info symbol 0x400cd0 |
整理如下,可以看到child中包含了两个指针,指向了Child类的vtable的不同偏移位置,这两个指针就是虚指针了。
| 地址 | 十六进制值 | 对应的symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0x7fffffffe1c0 | 0x400cd0 | vtable for Child + 16 |
| 0x7fffffffe1c8 | 0x0000000100000002 | Father::iPerson, Father::iFather |
| 0x7fffffffe1d0 | 0x400cf8 | vtable for Child + 56 |
| 0x7fffffffe1d8 | 0x0000000100000003 | Mother::iPerson, Mother::iMother |
| 0x7fffffffe1e0 | 0x0000000400000000 | Child::iChild, padding |
Child的vtable的内容
1 | (gdb) x/80xb 0x400cd0 - 16 |
整理如下:
| 内存地址 | 十六进制值 | symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0x400cc0 | 0x0000000 | top-offset(稍后说明) |
| 0x400cc8 | 0x400d80 | typeinfo for Child |
| 0x400cd0 | 0x400a6e | Person::helloPerson() |
| 0x400cd8 | 0x400ac8 | Father::helloFather() |
| 0x400ce0 | 0x400b98 | Child::helloChild() |
| 0x400ce8 | -16 | top-offset |
| 0x400cf0 | 0x400d80 | typeinfo for Child |
| 0x400cf8 | 0x400a6e | Person::helloPerson() |
| 0x400d00 | 0x400b22 | Mother::helloMother() |
child的vtable包含的内容包括:
top-offset: 对象起始地址与当前vptr所属子对象起始地址的偏移
1
2
3
4
5
6
7[cling]$ .L mutli-inher.cpp
[cling]$ Child child
(Child &) @0x7f963138b018
[cling]$ Father * pF = &child
(Father *) 0x7f963138b018
[cling]$ Mother * pM = &child
(Mother *) 0x7f963138b028从上面可以看到,当进行指针转换,将子类地址赋值给第二继承类的指针变量时,在这里则是将Child变量地址赋值给Mother指针变量时,需要用到vtable存储的top-offset,
pM = &child - (-16);top-offset与vptr的关系: top-offset = vptr[-2]
typeinfo: 当前类信息编译器开了RTTI,将会在vptr[-1]位置存储当前类的typeinfo对象;
virtual function: 最后是一些虚函数对应的地址;
- vptr[i]—当前类对应的第i个虚函数
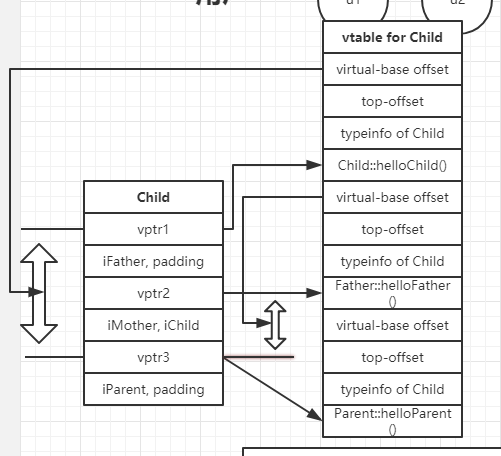
child变量与Child类的vtable的关系如下:
因此,vtable的作用包括了一下两点:
- 记录虚函数地址;
- 记录当前类的类型信息;
- 记录对象起始地址与子对象起始地址之间的偏移;
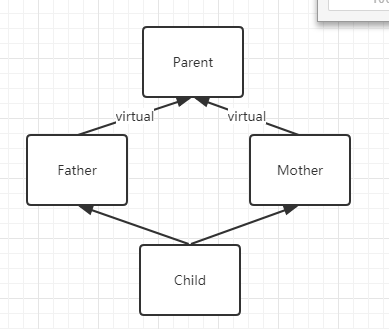
菱形继承–虚继承
在上面小节的继承体系下,child变量将会保存两份parent子对象,因而,导致了
1 | child.helloParent(); |
编译错误。通常情况下,我们并不希望在child中保存两份子对象,OOP中通过虚继承解决上面的问题
1 |
|
child 变量内存布局
1 | (gdb) p child |
可以看到,在使用了虚继承之后,Child的大小变成了48,对比上小节中child变量的内存布局,可以发现,多出来的8字节来自于Father子对象数据iFather以及Parent子对象iParent的内存对齐
通过 info symbol 查看child内存上面各个地址的对象:
| 地址 | 十六进制值 | 对应的symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0x7fffffffe1b0 | 0x400d58 | vtable for Child + 24 |
| 0x7fffffffe1b8 | 0x0000000000000002 | Father::iFather, padding |
| 0x7fffffffe1c0 | 0x400d80 | vtable for Child + 64 |
| 0x7fffffffe1c8 | 0x0000000300000004 | Mother::iMother, Child::iChild |
| 0x7fffffffe1d0 | 0x400da0 | vtable for Child+96 |
| 0x7fffffffe1d8 | 0x0000000100000000 | Parent::iParent, padding |
与前一节不同的是:
- Parent子对象被放置在整个对象靠后的地址
虚继承下,Child类的vtable
1 | (gdb) x/112xb 0x400d58 - 24 |
查看vtable的内容:
| 内存地址 | 十六进制值 | symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0x400d40 | 0x20 | virtual-base offset |
| 0x400d48 | 0x00 | top-offset |
| 0x400d50 | 0x400f60 | typeinfo for Child |
| 0x400d58 | 0x400acc | Father::helloFather() |
| 0x400d60 | 0x400c36 | Child::helloChild() |
| 0x400d68 | 0x10 | virtual-base offset |
| 0x400d70 | -16 | top-offset |
| 0x400d78 | 0x400f60 | typeinfo for Child |
| 0x400d80 | 0x400b8a | Mother::helloMother() |
| 0x400d88 | 0x00 | virtual-base offset |
| 0x400d90 | -32 | top-offset |
| 0x400d98 | 0x400f60 | typeinfo for Child |
| 0x400da0 | 0x400a0e | Parent::helloParent() |
虚继承情况下,Child的vtable与上一小节的vtable主要的不同在于:
- 增加了一个virtual-base offset用于记录共享子对象起始地址与当前对象起始地址之间的偏差
- 由于g++将共享子对象放置在整个对象靠后的地址,Parent与Child无法共享vptr,因此vtable增加了与Parent相关的信息